Delving into materials for windows, this introduction immerses readers in a unique and compelling narrative. From the durability of wood to the energy efficiency of vinyl, each material plays a crucial role in shaping the functionality and aesthetics of windows.
Let's embark on a journey to uncover the secrets behind choosing the perfect window materials for your space.
As we delve deeper into the world of window materials, we will explore the impact of different choices on energy efficiency, design, maintenance, and longevity. Get ready to discover everything you need to know about materials for windows in residential and commercial settings.
Types of Materials

Wood, vinyl, aluminum, and fiberglass are common materials used for windows in residential and commercial buildings. Each material has its own set of pros and cons in terms of durability, maintenance, and energy efficiency.
Wood
Wood windows offer a classic, traditional look and are known for their insulating properties. However, they require regular maintenance such as painting or staining to prevent rotting and warping.
Vinyl
Vinyl windows are low-maintenance and cost-effective. They are also durable and energy-efficient, but may not offer the same aesthetic appeal as wood windows.
Aluminum
Aluminum windows are lightweight, strong, and require minimal maintenance. They are also recyclable, but may not provide the best insulation compared to other materials.
Fiberglass
Fiberglass windows are extremely durable and low-maintenance. They are also highly energy-efficient and offer great insulation properties, making them a popular choice for many homeowners.
Energy Efficiency

When it comes to energy efficiency in buildings, the choice of window materials plays a crucial role. Different materials have varying impacts on how well a building retains heat in the winter and stays cool in the summer. This, in turn, affects energy consumption and costs associated with heating and cooling.
U-Factor and Its Significance
The U-factor is a measurement that indicates how well a window insulates against heat transfer. The lower the U-factor, the better the window is at preventing heat from escaping in the winter and entering in the summer. It is an important factor to consider when choosing energy-efficient window materials, as windows with lower U-factors can help reduce energy consumption and improve overall comfort in a building.
- Materials like double or triple-pane glass windows filled with insulating gas have lower U-factors compared to single-pane windows, providing better insulation.
- Low-E coatings can also help reduce heat transfer through windows, further improving energy efficiency.
Tips for Selecting Energy-Efficient Materials
When selecting window materials that offer better insulation and reduce heat loss or gain, consider the following tips:
- Look for windows with low U-factors to ensure better insulation and energy efficiency.
- Consider the climate in your area and choose materials that are suitable for the local weather conditions.
- Opt for double or triple-pane windows with insulating gas and Low-E coatings for enhanced energy efficiency.
- Check for ENERGY STAR ratings to identify windows that meet strict energy efficiency guidelines.
Design and Aesthetics

When it comes to the design and aesthetics of a building, the choice of window materials plays a crucial role in determining the overall look and feel. Different materials can greatly influence the style, ambiance, and functionality of a space.
Influence on Interior Ambiance
- Materials like wood can add warmth and a sense of coziness to a room, perfect for creating a rustic or traditional look.
- Metal frames, on the other hand, can lend a modern and sleek aesthetic, ideal for contemporary or industrial-style spaces.
- For a more minimalist approach, fiberglass or vinyl windows offer a clean and understated look that complements a variety of design styles.
Enhancement of Natural Light and Views
- Large windows with slim frames made from materials like aluminum can maximize natural light intake, creating bright and airy interiors.
- Choosing materials with durability and low maintenance, such as fiberglass, allows for expansive windows that offer unobstructed views of the outdoors.
Trends in Window Material Preferences
- Currently, there is a growing interest in sustainable and eco-friendly materials like recycled glass or reclaimed wood for a more environmentally conscious approach to design.
- Architectural trends favoring a seamless indoor-outdoor connection have led to an increased use of floor-to-ceiling windows with energy-efficient materials like insulated glass.
Maintenance and Longevity

Proper maintenance is crucial for the longevity of windows. Different materials require varying levels of care to ensure they last over time.
Maintenance Requirements for Various Window Materials
- Wood: Wooden windows need regular painting or staining to protect against moisture and rot. Periodic inspections for signs of decay are essential.
- Vinyl: Vinyl windows are low maintenance and only require occasional cleaning with soap and water to remove dirt and grime.
- Aluminum: Aluminum windows are durable but can corrode over time. Regular cleaning and applying protective coatings can help prevent this.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass windows are low maintenance like vinyl but may need occasional resealing to maintain their energy efficiency.
Comparing Durability of Different Materials
- Wood: While susceptible to rot, proper maintenance can extend the lifespan of wooden windows up to 30 years or more.
- Vinyl: Vinyl windows are known for their durability and can last around 20-40 years with minimal upkeep.
- Aluminum: Aluminum windows are prone to corrosion in coastal areas but can last 15-30 years with proper care.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass windows are highly durable and can last 20-40 years, making them a long-lasting option.
Tips for Extending Window Lifespan
- Regularly clean windows to remove dirt and debris that can cause damage over time.
- Inspect windows for any signs of wear or damage and address issues promptly to prevent further deterioration.
- Reapply sealants or coatings as needed to maintain energy efficiency and protect against the elements.
- Avoid using abrasive cleaners or tools that could scratch or damage the window surface.
Closure
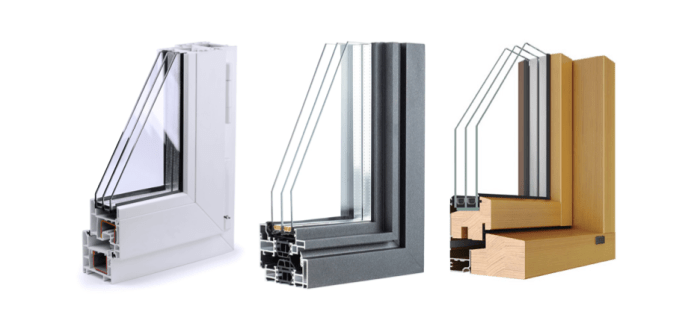
In conclusion, the choice of materials for windows is not just about aesthetics but also about functionality and sustainability. By understanding the intricacies of wood, vinyl, aluminum, and fiberglass, you can make informed decisions that enhance the beauty and efficiency of your living or working space.
Dive into the world of window materials and unlock a world of possibilities for your windows.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the most common materials used for windows?
The most common materials used for windows are wood, vinyl, aluminum, and fiberglass.
How do window materials impact energy efficiency?
Window materials can significantly impact energy efficiency by influencing factors like insulation, heat loss, and heat gain.
What maintenance practices can help extend the lifespan of windows?
Regular cleaning, proper sealing, and prompt repairs can all help extend the lifespan of windows made from various materials.